Troubleshooting Troubleshooting Guide for Unstable IoT Device Connections
Background
With the rapid development of smart home and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, more households and businesses are adopting IoT devices such as smart bulbs, smart plugs, thermostats, and security cameras. However, many IoT devices only support the 2.4GHz Wi-Fi band and often experience unstable connections, frequent disconnections, or failure to connect due to hardware limitations or firmware compatibility issues.
While the 2.4GHz band offers wider coverage, it is prone to interference (e.g., from microwaves, Bluetooth devices, or neighboring Wi-Fi networks). Additionally, some IoT devices struggle with modern router features (such as WPA3, MU-MIMO, or beamforming), leading to poor connectivity. This guide provides practical troubleshooting steps to optimize your network and improve IoT device stability.
Troubleshooting Steps
1. Create a dedicated 2.4GHz SSID for IoT devices
You may create one SSID combined with 2.4GHz, 5GHz and 6GHz operation with the same SSID name. However, IoT devices may not handle band-switching properly. To resolve this:
- Set up a separate 2.4GHz SSID (e.g., MyWiFi_IoT) and ensure IoT devices connect only to this network.
- Select WPA/WPA2-PSK (Auto) encryption instead of WPA3, as some older IoT devices may not support it.
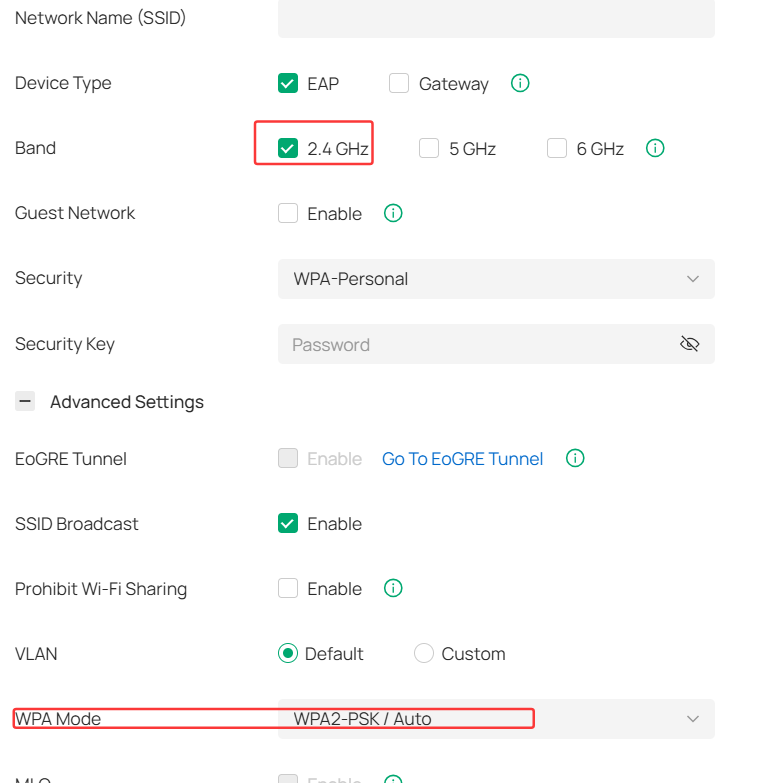
2. Disable advanced wireless features
IoT devices often use low-power, low-cost Wi-Fi modules that may not support advanced functionalities. Check and disable the following in your WLAN settings:
- WPA3 encryption (switch back to WPA2 if enabled)
- PMF choose as Disable
- Uncheck 802.11r
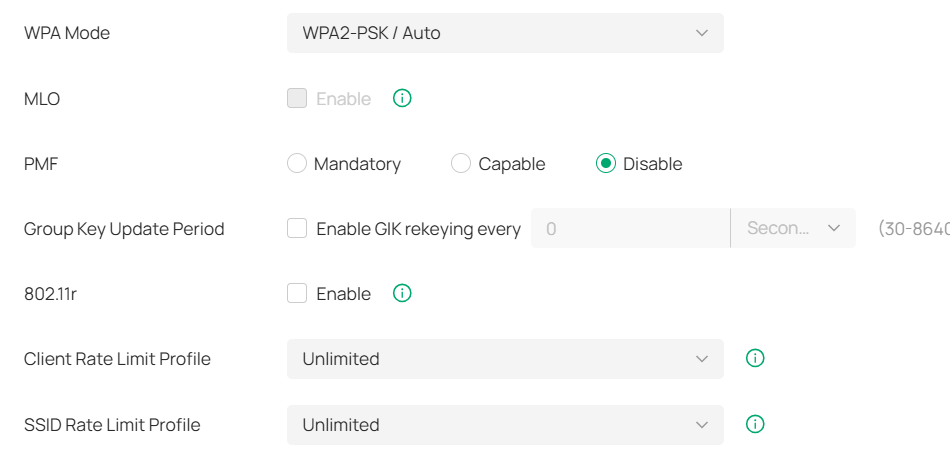
- 20/40MHz channel auto-switching (set to 20MHz to reduce interference)
- Uncheck all the options under Multicast/Broadcast Management (They are enabled by default)

3. Optimize Wi-Fi channels to minimize interference
The 2.4GHz band has only three non-overlapping channels (1, 6, and 11). If nearby networks are congested:
- Use a Wi-Fi analyzer app (e.g., WiFi Analyzer) to scan for the least crowded channel.
- Manually select a less congested channel (1, 6, or 11) in your router settings.
4. Update IoT device and EAP firmware
- Check for firmware updates for your IoT devices (manufacturers often release fixes for Wi-Fi compatibility issues).
- Update your EAP firmware to ensure better device support and stability.
5. Adjust device placement
- Ensure IoT devices are not obstructed by walls, metal objects, or other barriers.
- If the signal is weak, consider using a Wi-Fi extender or a mesh network to improve coverage.
If the problem persists
If your IoT device still experiences unstable connections after following these steps:
1. Post a new thread in a community or forum or contact TP-Link support, providing:
- IoT device model and firmware version
- EAP model and firmware version
- Screenshots of SSID settings (including encryption and channel)
- Detailed issue description (e.g., frequent disconnections, how to recover, screenshots of the IOT APP when disconnected)
2. Contact the device manufacturer or your ISP's technical support for further assistance.
Conclusion
Most IoT connectivity issues stem from compatibility problems or network interference. By optimizing your settings, you can often resolve these issues. If you still encounter problems, feel free to leave a comment or contact technical support - we're here to help!
Recommended Threads:
How to optimize wireless performance of EAP products
Experience the Latest Omada EAP Firmware - Trial Available Here, Subscribe for Updates!
Feedback:
- If this was helpful, welcome to give us Kudos by clicking the upward triangle below.
- If there is anything unclear in this solution post, please feel free to comment below.
Thank you in advance for your valuable feedback!
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Have other off-topic issues to report?
Welcome to > Start a New Thread < and elaborate on the issue for assistance.
