How to configure Multiple SSIDs with Multiple Subnets on EAP products
Applies to: EAP Products
In an enterprise network, we usually need to divide the network into different VLANs to isolate broadcast domains, reducing the impact of interference on the network's performance. The enterprise network is typically divided by departments, such as R&D, Marketing, Product, etc. Now that wireless devices like smartphones and laptops are being used more frequently in office environments, the IT department has to configure each VLAN with a different wireless network (SSID) to meet these office needs.
In this document, we provide a simple, step-by-step guide to configuring this setup using a TP-Link SMB router/switch and EAPs.
Required devices:
EAP Products, such as EAP225
L2+or L3 Switches, such as T2600-28TS
Multi-net NAT Available Routers, such as TL-ER6120
Topology:
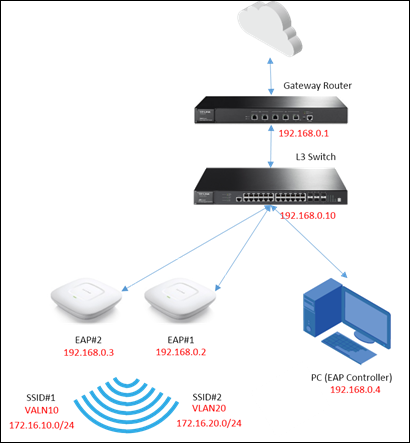
Step 1: Configure Multi-Nets NAT and Static Route on the Gateway Router
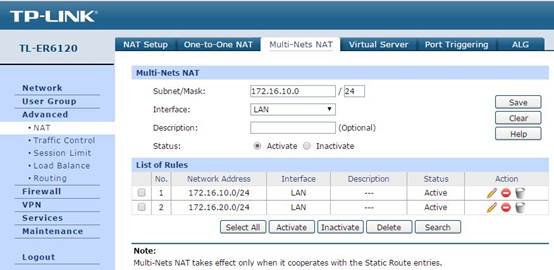
(1)Multi-Nets NAT Configuration:
Since multiple subnets require NAT functionality, the gateway needs to support Multi-Nets NAT. In the gateway router’s Web UI, you can configure it in Advanced -> NAT -> Multi-Nets NAT as the figure shows below.
Configure the IP and subnet mask of each subnet and leave Interface as LAN for each network.
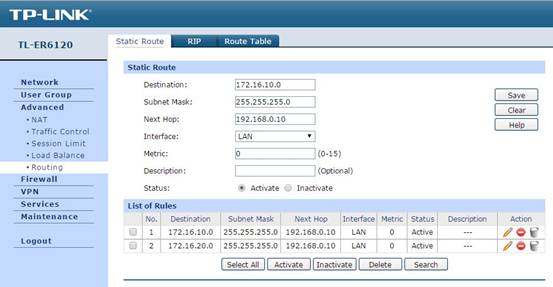
(2)Static Route configuration
In Advanced -> Routing -> Static Route, configure the static route, which helps the data packet from the WAN find the next hop, the L3 switch. Set Destination to the subnet’s network address, Next Hop to the switch’s IP, and Interface to "LAN".
The configuration on the gateway router is done. Next we will configure the switch.
Step 2: Configure VLAN and Port Attribute on Switch
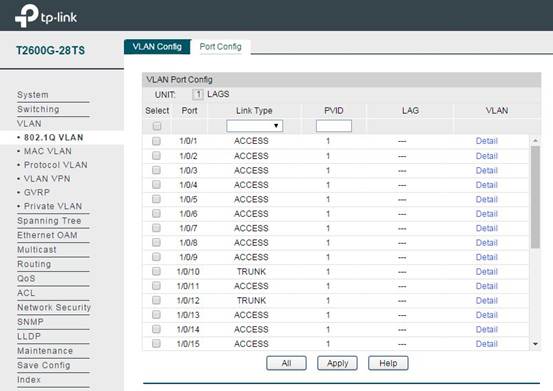
(1)Port Attribute Configuration:
In VLAN -> 802.1q VLAN -> Port Config, set the ports connected to EAP as Trunk mode (Port 1/0/10 and 1/0/12 in this topology). The port in Trunk mode can transmit data packets with different VLAN tags. Set PVID as 1.
(2)VLAN Configuration
In VLAN -> 802.1q VLAN -> VLAN Config, add the ports connecting the switch and EAP to the VLAN. Here we use VLAN 10 and VLAN 20 as examples.VLAN10 and VLAN20 both have member ports 1/0/10 and 1/0/12.
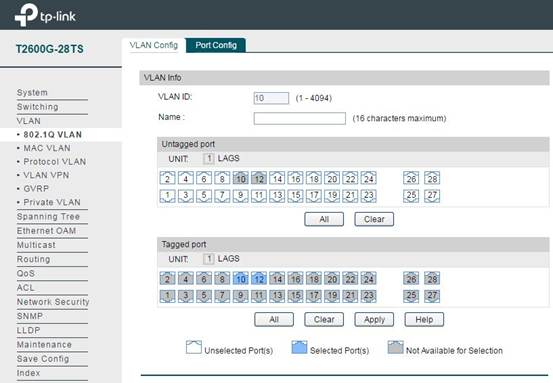
Step 3: Configure L3 Interface and DHCP Server for VLAN on Switch.
(1)VLAN’s L3 Interface Configuration:
In Routing -> Interface -> Interface Config, add an L3 interface for the VLAN configured in previous steps. This allows the VLAN to communicate like a normal subnet on IP Layer. IP Address Mode should be set to Static. IP Address and Subnet Mask specify the default gateway and network size for the subnet.
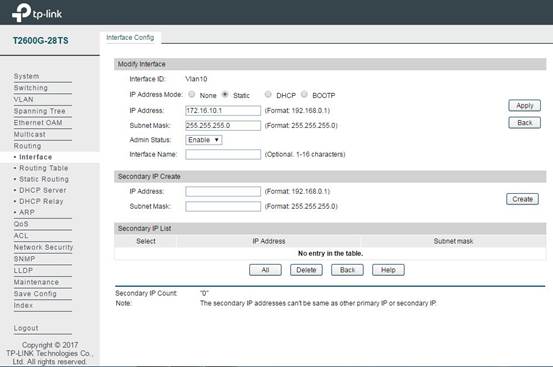
(2)DHCP Server Configuration for each subnet:
After configuring the L3 interface for VLAN, we also need to set up a DHCP Server for each subnet to assign IPs for the wireless clients. In Routing -> DHCP Server -> Pool Setting, you can configure an IP address pool for each subnet. Network Address and Subnet Mask specify the size of the address pool. Default Gateway specifies the default gateway for the subnet to which the address pool is bound. The DNS server specifies the corresponding DNS server. These configurations will be sent to the clients during DHCP process.
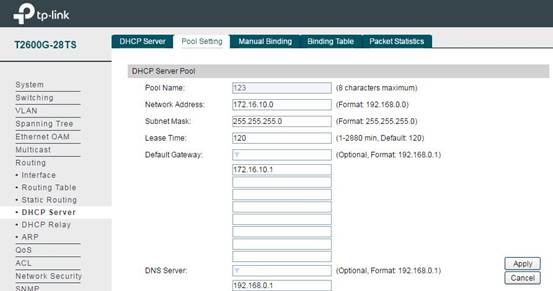
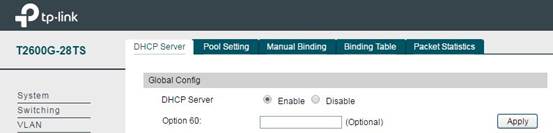
Note: The DHCP Server is disabled by default, so after configuring the DHCP address pool, please don’t forget to enable the DHCP Server. Without this, your wireless devices connected to the SSID will not be able to obtain an IP address.
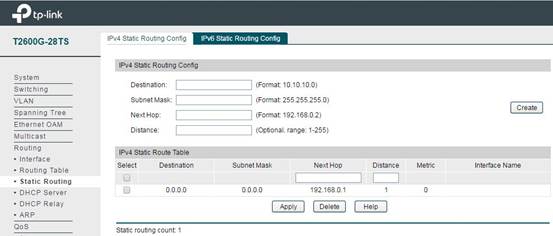
Step 4: Static Route Item Configuration on Switch
In Routing -> Static Routing -> IPv4 Static Routing Config, you can add the static route items, as the following figure shows. The purpose of this static route item is to forward all the data packets received by the switch to the front gateway router successfully. So the Destination IP 0.0.0.0 means any data packets with any destination IP will be forwarded to 192.168.0.1 (the gateway router).
Now, the configuration on the Switch is complete. Lastly, we will configure the EAP.
Step 5: Configure SSID items with VLAN ID on EAP Controller
Run EAP Controller and after successfully Adopt EAP, add new SSID in Setting -> Wireless Settings. Add the previously configured VLAN ID in the Wireless VLAN ID section.
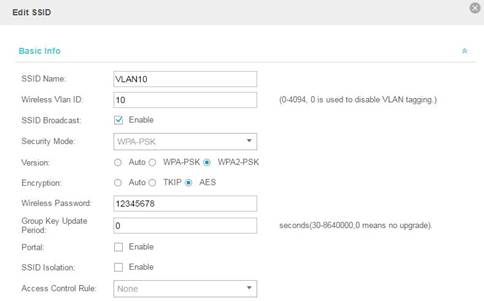
Configure two SSIDs, name them as VLAN10 and VLAN20. Use the terminal device to connect the two SSIDs and we can see the IP addresses assigned to the terminal device are 172.16.10.3 and 172.16.20.3. And the terminal can access the Internet which means the configuration has been successful.
